What is Paralysis?
In Ayurveda, paralysis is generally referred to as "Pakshaghata," which can be loosely translated to "hemiplegia" in modern medical terminology. Pakshaghata is a neurological disorder that involves the loss of strength and function on one side of the body, often affecting the arm and leg on that side. This condition is akin to hemiplegia in Western medicine, which results from damage to the brain or nervous system, leading to a loss of motor function and control on one side of the body.
Ayurveda considers Pakshaghata to be primarily caused by an imbalance in the Vata dosha (one of the three fundamental bio-energies in Ayurvedic philosophy), leading to impaired circulation and nerve function. This imbalance can be caused by various factors, including poor lifestyle choices, dietary habits, stress, and genetic predisposition.
Ayurvedic treatment for Paralysis involves a holistic approach that aims to balance the disrupted Vata dosha and promote overall health and well-being.
Causes of Paralysis
Paralysis is the loss of muscle function in part of your body. Let’s delve into the Paralysis causes. It can occur due to a variety of underlying causes, and these causes can be broadly categorized into 2 main types:
- Central Nervous System Causes
-
Peripheral Nervous System Causes
1. Central Nervous System (CNS) Causes: The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. Paralysis resulting from issues within the CNS is often more widespread and severe.
- Stroke: A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, leading to damage or death of brain cells. This can result in paralysis on one side of the body (hemiplegia) or affect specific body parts depending on the location of the stroke.
- Spinal Cord Injury: Trauma to the spinal cord can lead to paralysis. The level of paralysis depends on the location and severity of the injury. Injuries higher up on the spinal cord can lead to more extensive paralysis.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Severe head injuries can damage the brain and result in paralysis. The extent of paralysis depends on the area of the brain affected.
- Tumors: Cancerous or non-cancerous tumors in the brain or spinal cord can compress or damage nerve cells, leading to paralysis.
- Infections: Certain infections, like spinal cord infections or encephalitis, can damage the nervous tissue and cause paralysis.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Causes: The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Paralysis from PNS causes might be more localized.
- Peripheral Nerve Injury: Trauma, such as a serious injury or compression, can damage peripheral nerves and lead to paralysis of the muscles they innervate. Examples include carpal tunnel syndrome or nerve injuries in accidents.
- Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy involves damage to peripheral nerves due to conditions like diabetes, alcoholism, or certain medications. This can result in muscle weakness and paralysis over time.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: This autoimmune disorder affects peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis. It often starts in the legs and can progress to other parts of the body.
- Botulism: Botulism toxin affects the nerves responsible for muscle contraction, leading to paralysis. It can result from contaminated food or wounds.
- Myasthenia Gravis: This autoimmune disorder affects neuromuscular junctions, causing muscle weakness and fatigue that can progress to paralysis, particularly in the face and throat.
Other Causes of Paralysis
- Genetic Conditions: Certain genetic disorders can result in paralysis, such as muscular dystrophy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) involve the immune system attacking the protective covering of nerve fibres, leading to paralysis.
- Metabolic Disorders: Disorders like porphyria or periodic paralysis can cause temporary episodes of paralysis due to abnormal metabolic processes.
How can you treat Paralysis with Shri Chyawan Ayurveda’s Paralysis Care Kit?
Shri Chyawan Ayurveda has formulated Paralysis Care Kit, the best ayurvedic medicine for paralysis treatment using purely herbal and ayurvedic ingredients causing zero side-effects. This kit is extremely effective in all types of Joint, muscle related pain and is the most used paralysis medicine in Ayurveda. In short it is a complete Paralysis Treatment.
Product Benefits:
1. Life Guard Advance is multivitamin syrup; it provides all the necessary vitamins needed by our body during pregnancy or anemia. It helps to boost the immunity power.
2. Anart Powder helps in reducing the swelling in the joints giving you relief from the pain.
3. Peedago Vati is an Ayurvedic Painkiller; unlike the others available in the market Peedago Vati does not have any side effects.
4. Shilajit Vati helps to increase durability & strengthen the body.
5. Right King Oil massage lightly with this oil which helps to relieve pain and relaxes muscles.
6.Chandraprabha Vati helps in reducing physical stress and helps your body to relax.
Key Ingredients:
-
Life Guard Advance: It contains natural ayurvedic ingredients like Arjun Chal, Ashwagandha, Gokhru, Satvari, Utangan, Shilajeet, Tulsi, Salimpanja, Amla, Harde, Baheda, Sauth, Mari, Pipal.
-
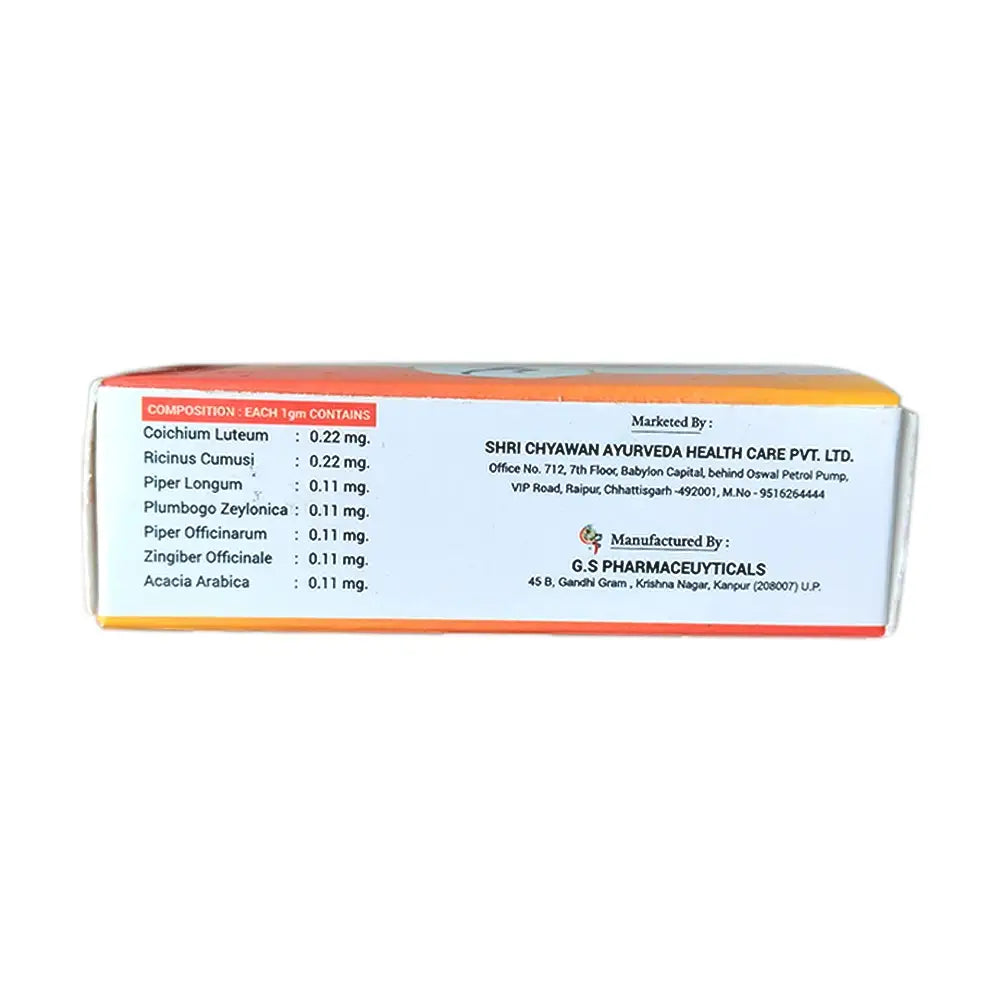
Anart Powder: It contains natural ayurvedic ingredients like Ricinus Communis, Colchicum luteum, Pipali, Chitrak Haritaki, Ginger, Vinarghya, Piper Offcinarum.
-
Peedago Vati: It contains natural ayurvedic ingredients like Shudh Kuchl, Bhilawa, Ajmod, Terminalia Chebula, Black Pepper, Badheda, Ajmod, Nagarmotha.
-
Shilajit Vati: It contains natural ayurvedic ingredients like Siddh Makardwaj, Semal Musli, Safed Musli, Punarnava, Salim Panja, Akarkara, Utangan, Moch Ras, Kali Musli, Shilajit.
-
Right King Oil: It contains natural ayurvedic ingredients like Neem, Sehjan, Chopchini, Ashwagandha, Peppermint, and Kapur.
- Chandraprabha Vati: It consists SwarnBhasm, VaiVidang, Chitrak Bark, Daruharidra, Devdaru, Camphor, Pipalmool, Nagarmotha, Pippal, Kali Mirch, Yavkshar, Vach, Dhania, Chavya, Gajpipal, Sounth, SendhaNamak, Nishoth, Dantimool, Tejpatra, Chhoti elaichi.
How to use:
1. Life Guard Advance - 10ml two times a day after meal i.e., lunch and dinner.
2. Anart Powder - Every morning and evening after breakfast and snacks respectively.
3. Peedago Vati - Every morning and evening after breakfast and snacks respectively.
4. Shilajit Vati - One tablet twice a day after meals.
5. Right King Oil - Massage with the oil twice every day.
6. Chandraprabha Vati -One tablet twice a day, after a meal i.e., lunch and dinner.
Other treatment methods in Ayurveda:
-
Panchakarma Therapy: This is a series of detoxification and rejuvenation therapies that help balance the doshas and remove toxins from the body. Specific therapies, such as Abhyanga (oil massage), Shirodhara (pouring of warm oil on the forehead), and Basti (medicated enema), can be employed.
-
Herbal Remedies: Ayurvedic practitioners often prescribe herbal formulations to support nervous system health and promote circulation. These formulations may include herbs like Ashwagandha, Brahmi, Guggulu, and Dashmula.
-
Diet and Lifestyle Changes: A balanced diet that includes warm, easily digestible foods is recommended. Avoiding cold and heavy foods can help pacify Vata dosha. Adequate rest, stress management, and gentle exercise are also important.
-
Yoga and Meditation: Gentle yoga postures and pranayama (breathing exercises) can help improve blood circulation and promote relaxation. Meditation and mindfulness practices can aid in reducing stress and anxiety.
- Ayurvedic Therapies: Specific therapies like Nasya (nasal administration of medicated oils), Kati Basti (medicated oil application on the lower back), and Pinda Sweda (herbal bolus massage) might be employed to address the condition.
In conclusion, Ayurveda offers a holistic approach to treating paralysis, focusing on restoring balance within the body and mind. Through personalized therapies, herbal remedies, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes, Ayurveda aims to address the root causes of paralysis rather than merely alleviating symptoms. It emphasizes the importance of harmony between the doshas, proper digestion, detoxification, and strengthening of the nervous system.