In Ayurveda, fatty liver is generally understood as "Yakrit Vriddhi" or "Yakrit Adhoomani." The liver, or "Yakrit" in Sanskrit, is considered a crucial organ responsible for various metabolic activities. According to Ayurveda, an accumulation of excess fat in the liver disrupts its functions and is attributed to an imbalance in the body's doshas, primarily the "Pitta" dosha.
Fatty Liver Causes:
-
Dietary Habits: Consuming excessive oily, fatty and heavy foods, along with processed or junk food, can disturb the balance of Pitta and contribute to fatty liver.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity or a sedentary lifestyle can hamper proper metabolism and lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
-
Imbalanced Digestion: Weak digestion or irregular eating habits can impact the body's ability to metabolize fats properly, leading to their accumulation in the liver.
-
Toxin Build-up: Exposure to environmental toxins, consumption of alcohol, or intake of certain medications without proper purification can contribute to liver issues in Ayurveda.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Imbalances in hormonal levels, especially related to metabolism, can influence fat accumulation in the liver.
Fatty Liver & Other Diseases:
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) encompasses a range of liver conditions characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells, unrelated to excessive alcohol consumption. It's considered a spectrum because it includes various stages of severity, with two primary stages being:
-
Simple Fatty Liver (Steatosis): This is the initial stage of NAFLD where there is an accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It typically doesn't cause major liver damage and might not show noticeable symptoms in many cases.
-
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): NASH is a more severe form of NAFLD. It involves not only the accumulation of fat but also inflammation and liver cell damage. This stage has the potential to progress to more severe conditions like fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer.
-
Fatty Liver & Liver Cirrhosis: Fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis are interrelated conditions, with cirrhosis being an advanced stage that can result from the progression of fatty liver disease in some cases.
-
Fatty Liver Disease: This condition involves the accumulation of excessive fat in liver cells. It's often linked to various factors such as obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and excessive alcohol intake. Fatty liver disease exists in different stages, starting with simple steatosis (accumulation of fat without inflammation) and potentially progressing to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), characterized by liver inflammation and cell damage.
- Liver Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is an advanced and irreversible stage of liver disease marked by extensive scarring of liver tissue. The scarring disrupts the normal structure and function of the liver. Chronic liver damage from various causes such as chronic alcohol abuse, chronic viral hepatitis (like hepatitis B and C), autoimmune diseases, or long-standing untreated fatty liver disease (especially NASH) can lead to cirrhosis.
Not everyone with fatty liver disease progresses to cirrhosis, but prolonged or severe liver damage and inflammation increase the risk. In some cases, particularly in individuals with NASH or severe and ongoing liver injury, fatty liver disease can progress to cirrhosis over time. This progression involves a gradual process where persistent liver damage causes scar tissue to replace healthy liver cells.
Fatty Liver & Cardiovascular Disease: Fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease (CVD) are interconnected in several ways, and individuals with fatty liver disease often have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular issues.
Here are some connections between fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease:
-
Shared Risk Factors: Fatty liver disease is frequently associated with conditions like obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and dyslipidemia (abnormal levels of lipids in the blood), all of which are significant risk factors for cardiovascular disease. These shared risk factors contribute to the increased likelihood of developing both conditions.
-
Systemic Inflammation: Fatty liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its more severe form, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), involves liver inflammation. This systemic inflammation can lead to increased levels of inflammatory markers in the bloodstream, contributing to atherosclerosis (hardening and narrowing of arteries), a key factor in cardiovascular disease.
-
Impact on Lipid Metabolism: Fatty liver disease can disrupt lipid metabolism, leading to alterations in lipid profiles (such as increased triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) that are associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease.
-
Association with Metabolic Syndrome: Fatty liver disease is often considered a component of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type2 diabetes. Metabolic syndrome includes obesity, insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and abnormal lipid levels.
- Liver Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Health: Severe forms of fatty liver disease, especially when it progresses to cirrhosis, can impact the liver's ability to produce proteins essential for blood clotting and other cardiovascular functions. This dysfunction can indirectly affect heart health and circulation.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Fatty Liver:
Our Liver Care Kit is the best fatty liver ayurvedic treatment and it has been formulated to primarily focus on problems related to non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases, alcohol-related liver diseases, Hepatitis, Hemochromatosis, etc. and it effectively provides relief. This kit is made using all herbal and natural ingredients and is safe to use. It consists of:
- Chandraprabha Vati:
It reduces the level of Uric acid, which ultimately helps to provide relief from the pain in the liver and reduces swelling as well.
Ingredients:
It consists Swarn Bhasm, Vai Vidang, Chitrak Bark, Daruharidra, Devdaru, Camphor, Pipalmool, Nagarmotha, Pippal, Kali Mirch, Yavkshar, Vach, Dhania, Chavya, Gajpipal, Sounth, Sendha Namak, Nishoth, Dantimool, Tejpatra, Chhoti elaichi.
How to use: Consume 1 tablet at night before going to bed.
- Panch Tulsi Drops: Shri Chyawan Ayurveda's Panch Tulsi Drops have been made with 5 forms of Tulsi that is Ram Tulsi, Van Tulsi, Shyam Tulsi, Vishnu Tulsi and Nimu Tulsi. It helps boost the immune system and build body's resistance. This drop is very effective to fight normal cold, cough, sore throat, etc.
Ingredients: Panch Tulsi Drops consist of extract of 5 types of tulsi namely: Ram Tulsi, Van Tulsi, Shyam Tulsi, Vishnu Tulsi, and Nimu Tulsi. It does not include any artificial colors, flavors, etc.
How to use: Add 1-2 drops of Panch Tulsi Drops in a cup of tea/coffee or in a glass of water, twice a day.
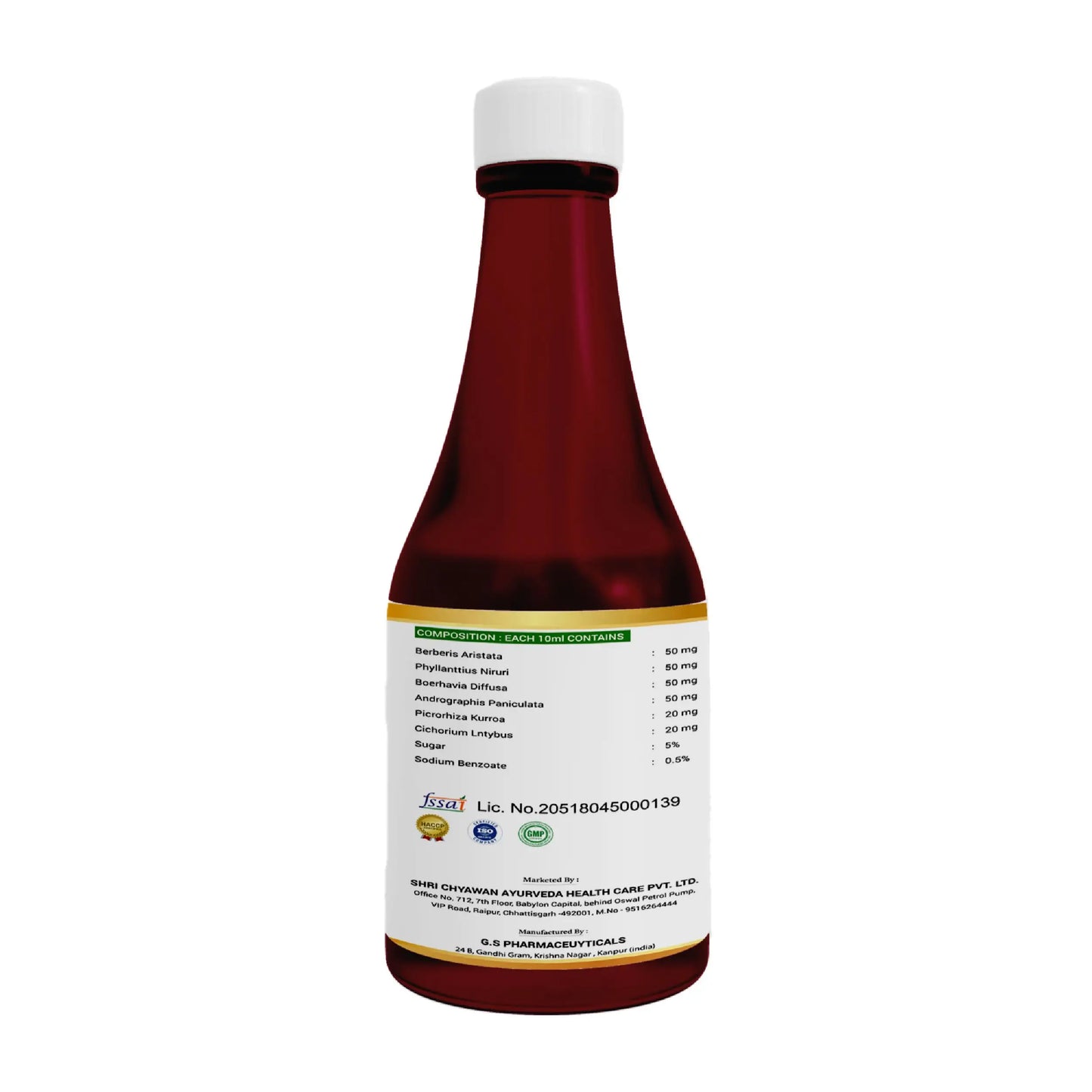
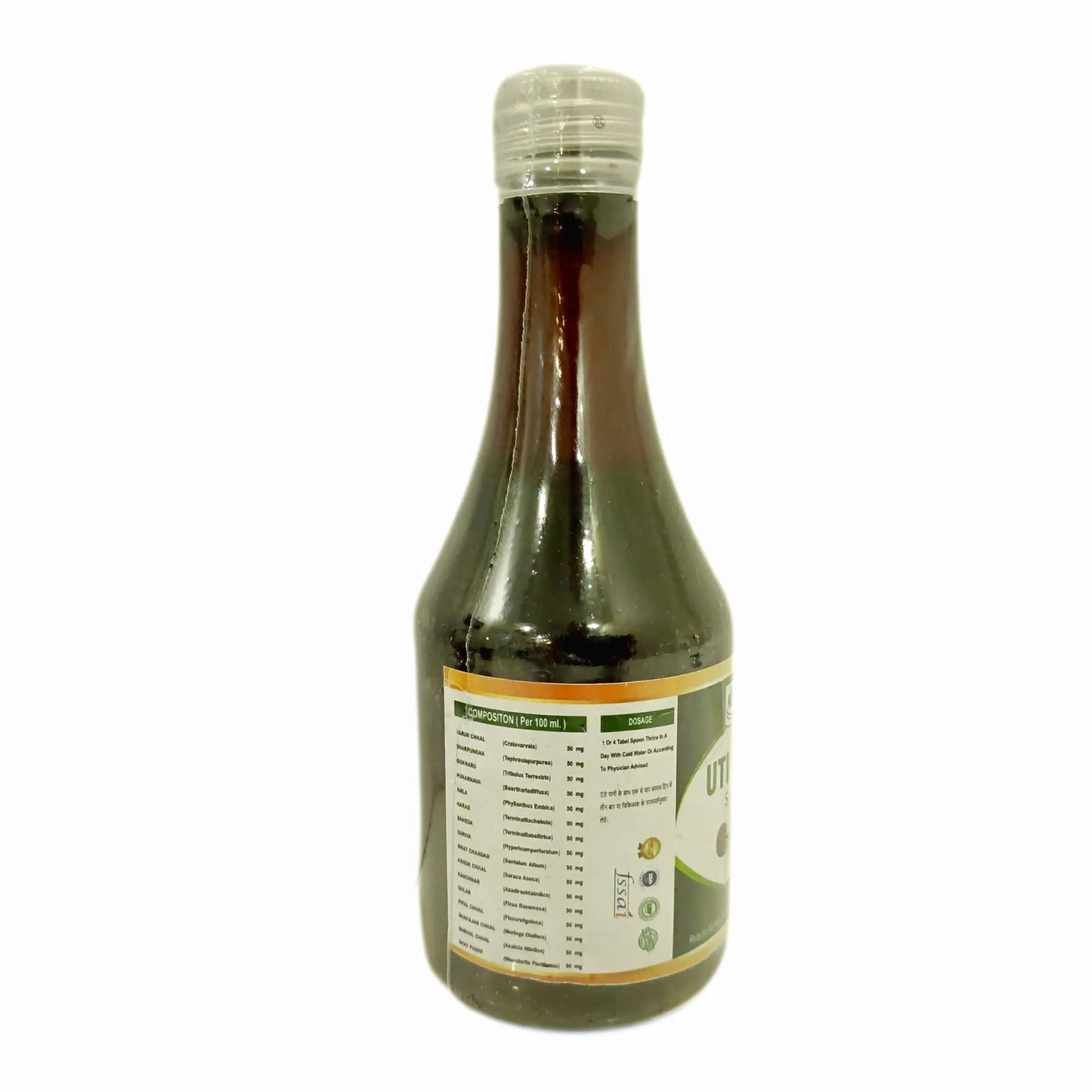
- Uti Care Syrup: It is useful in Urine Infection and Urine blockages. It also acts as a detoxifier for your body and cleanses your system.
Ingredients: It consists of mainly Varun Chal, Sharpunkha, Gokharu, Punarnava, Amle, Harde, Baheda, Sariva, Swat Chandan, Ashok Bark, Kanchanar, Gullar Fruit, Pipar Bark, Drumstick Bark, Babbol Bark, Dhatkipuspa.
How to use: Consume 1 teaspoon thrice a day with cold water or as directed by the physician.
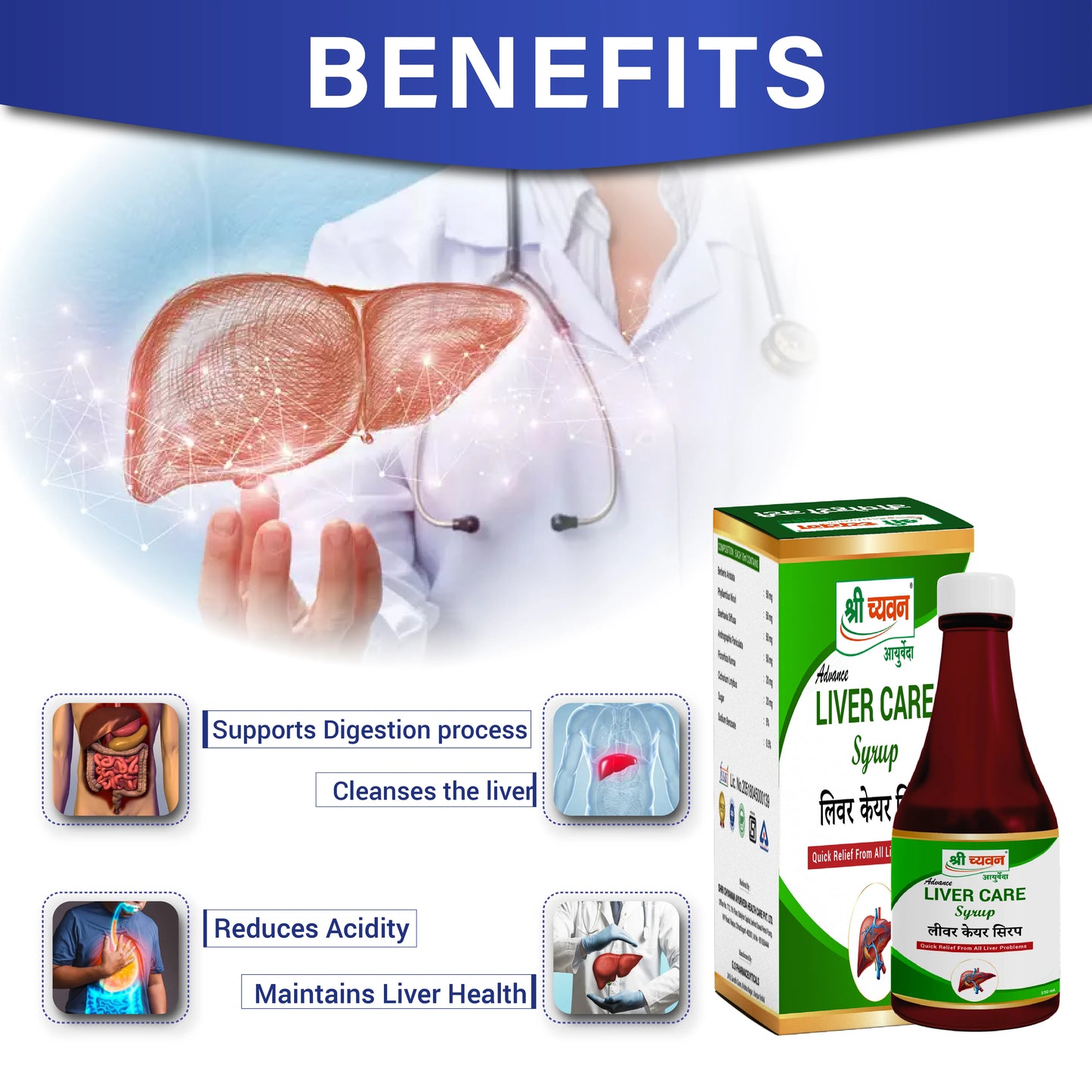
- Liver Care Syrup: One of the best ayurvedic syrup for fatty liver formulated to cleanse your liver. It also helps to strengthen the overall functioning of the liver.
Ingredients: It consists of Chitrakmul, Amla, Harde, Baheda, Bel Patra, Dhana, Aloe vera, Ajwain, Punarnava, Giloy Satva, Neem Chal, and Tulsi.
How to use: Consume 1-2 teaspoonful of Liver Care Syrup, thrice a day or as suggested by your physician.
Other Treatment Approaches:
-
Dietary Modifications: Following a Pitta-pacifying diet that includes fresh, easily digestible foods, incorporating bitter and astringent tastes, and reducing heavy, oily, and fried foods.
-
Herbal Remedies: Using herbs like kutki, punarnava, triphala, turmeric, and bhumyamalaki, which are believed to support liver health and aid in fat metabolism.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Encouraging regular physical activity, yoga, and pranayama to improve digestion, metabolism, and overall health.
-
Detoxification (Panchakarma): Undergoing Panchakarma therapies like Virechana (therapeutic purgation) or Basti (enema therapy) to eliminate toxins and balance the doshas.
- Stress Management: Stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and adequate rest are considered essential in Ayurveda for overall well-being and liver health.
Ayurvedic treatment for fatty liver disease involves a holistic approach. Embracing a balanced, nutrient-rich diet, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise, avoiding excessive alcohol intake, and managing underlying conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol are pivotal. Additionally, regular medical check-ups, monitoring liver health, and seeking professional guidance are crucial for personalized care. Prioritizing these precautions can significantly reduce the progression and complications of fatty liver disease, promoting overall well-being.